Overview
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a type of medical imaging that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce in-depth pictures of the inside of the body. Pregnancy, organ damage, and internal traumas are just a few of the illnesses that can be diagnosed and monitored using these images.
Types of ULTRASOUND
There are numerous varieties of ultrasonography, and each one serves a particular function. The following are a few of the most typical ultrasound types:
- Transabdominal ultrasound: This kind of ultrasound is used to look within the abdomen to assess the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. Usually, a gel is applied to the skin before sending and receiving sound waves with a transducer, a handheld device.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This kind of ultrasound is used to look at the uterus and ovaries in women, as well as other female reproductive organs. A transducer is inserted into the vagina to perform it. This kind of ultrasound is frequently performed in the first trimester of pregnancy to confirm the foetus’ gestational age and look for any anomalies.
- Obstetric ultrasound: This kind of ultrasound is used to look at a growing foetus when the mother is pregnant. The due date, the presence of other pregnancies, and any anomalies or issues with the pregnancy can all be determined using this test.
- Doppler ultrasound: With this sort of ultrasonography, blood flow through arteries is measured using sound waves. It can be used to identify blood clots, obstructions, or other circulatory system issues.
- Echocardiography: This type of ultrasonography employs sound waves to produce images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels. It can be used to identify and track cardiac diseases like congenital heart defects, heart disease, and issues with the heart’s valves.
- High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU): With the help of powerful sound waves, this type of ultrasound can shrink or obliterate bodily tissue. It is used to treat a number of ailments, including kidney stones and uterine fibroids.
- Elastography: In this form of ultrasound, sound waves are used to produce images that display the tissue’s rigidity. It is used to identify and keep track of problems like thyroid nodules, breast cancer, and liver illnesses.
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasound: This type of ultrasound makes blood vessels and organs more visible by using microbubbles as contrast agents. It can be used to find anomalies like tumors.
Each kind of ultrasound provides a distinctive view into the human body and can be utilised in tandem to paint a more thorough and comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition.
PROCEDURE of ULTRASOUND
The general ultrasound procedure can be described as follows:
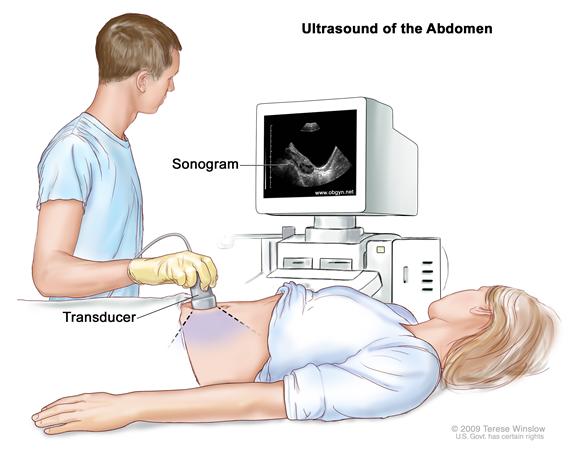
- The patient normally lies down on a table to begin the ultrasound procedure. A gel is placed on the skin over the area being studied to make the sound waves pass through the skin more easily.
- Next, a hand-held instrument called a transducer is moved across the gel-coated region. The transducer emits ultrasonic waves, which are high-frequency sound waves, which enter the body and reflect off of internal organs.
- The transducer gathers the echoes and transmits them to a computer, which produces precise images of the interior of the body. The technician or doctor can check out the area of interest by looking at these images in real time on a screen.
- During some ultrasound scans, the patient may be asked to hold their breath or drink water so that the doctor can see the gallbladder or kidneys better.
- The gel will be removed after the procedure, and the patient can resume their regular activities. The process might last anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour, depending on the sort of test and the part of the body being examined.
ADVANTAGES
With several advantages over other imaging modalities, ultrasound is a frequently used medical imaging tool. The following are a few of the main benefits of ultrasound:
- Non-invasive: Since ultrasound does not require any incisions or injections, it is a non-invasive procedure. Patients now have a safer and more pleasant option, especially if they are expecting or have a fear of needles.
- Real-time imaging: Ultrasound creates images that are visible to the technologist or doctor while the body’s interior organs move. This makes it a great tool for keeping track of how certain illnesses or therapies are doing.
- Versatile: The heart, blood vessels, gastrointestinal organs, reproductive organs, and musculoskeletal system can all be examined using ultrasound.
- Safe: Because ultrasound doesn’t use ionising radiation, there is no chance of getting exposed to radiation.
- Cost-effective: Since ultrasound is a relatively inexpensive imaging technology, more patients may utilise it.
- Portable: Ultrasound machines are portable, so they can be brought to the patient’s bedside for patients who are confined to their beds or who are located in distant areas.
- Guiding procedures: Ultrasound can be used to guide certain procedures, such as biopsies and aspirations, making them safer and more accurate.
- Dynamic evaluation: Ultrasound can be used to evaluate blood flow and tissue flexibility, giving important details about how well organs and blood vessels are working.
Overall, ultrasound is a useful diagnostic tool that gives doctors the knowledge they need to choose the best course of treatment for their patients. It is the perfect diagnostic tool for a variety of medical diseases because of its non-invasiveness, real-time imaging, adaptability, safety, affordability, and portability.
Machines Available For Ultrasound At MSDC
At MSDC, we use the most advanced ultrasound technology to give our patients the finest care possible. The Siemens X 300 PE, Siemens NX2, and Mindray DC 70 ultrasound equipment are a few of the technologies we use. These tools enable us to swiftly and effectively produce photos of the highest quality.
The Siemens X 300 PE is a high-end ultrasound machine that generates high-resolution images that are perfect for diagnostic use. It has cutting-edge capabilities like real-time image processing that makes it simple to use and help lower the possibility of human error. The device also has a number of transducers that enable it to be used for a wide range of applications, including musculoskeletal, cardiology, and obstetrics.
The Siemens NX2 is a flexible ultrasound device created for use in a variety of clinical settings. It has cutting-edge capabilities like real-time image processing that makes it simple to use and help lower the possibility of human error. Additionally, the device contains a variety of transducers, enabling a wide range of applications, including obstetrics, gynaecology, cardiology, and musculoskeletal.
The compact, user-friendly Mindray DC 70 ultrasound scanner is intended for usage in a variety of therapeutic settings. It has cutting-edge capabilities like real-time image processing that makes it simple to use and help lower the possibility of human error. Additionally, the device contains a variety of transducers, enabling a wide range of applications, including obstetrics, gynaecology, cardiology, and musculoskeletal.
The Siemens X 300 PE, Siemens NX2, and Mindray DC 70 ultrasound devices work together to swiftly and effectively produce high-quality images. These devices provide images that are easy to share with other medical experts and that can be used to diagnose a variety of illnesses. We have a skilled team of experts who are trained to use these tools, and they would be pleased to answer any questions you may have.