Overview
Foetal medicine is a subspecialty of obstetrics that focuses on the identification and treatment of illnesses and abnormalities in developing foetuses. It entails the use of cutting-edge imaging methods, such as ultrasound, to generate precise images of the foetus, as well as genetic testing and other diagnostic tools to detect and identify a wide range of foetal diseases.
TECHNIQUES INVOLVED IN FOETAL MEDICINE
Some of the main techniques used in foetal medicine are listed below:
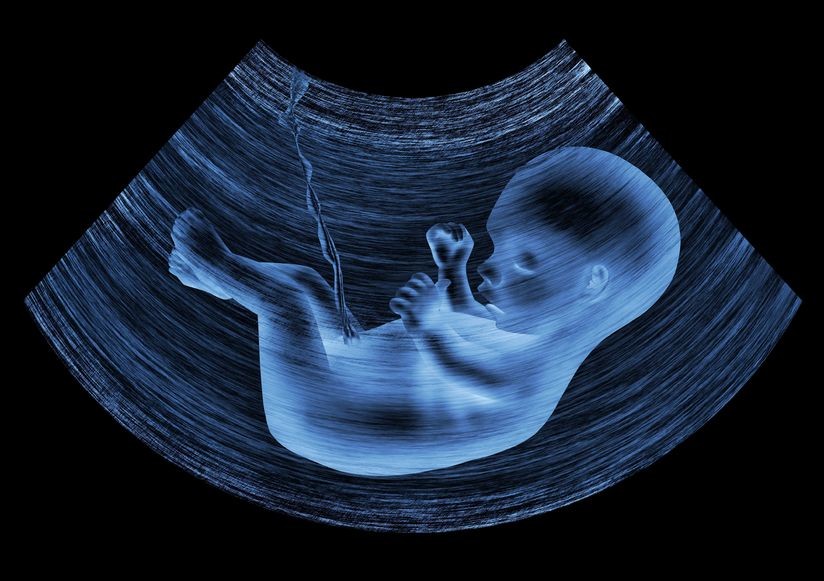
- Ultrasound: The most popular diagnostic device in foetal medicine is ultrasound. It produces finely detailed photographs of the foetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid using high-frequency sound waves. Numerous foetal disorders, including chromosomal abnormalities, structural flaws, and growth limitations, can be identified using ultrasound.
- Amniocentesis: During an amniocentesis, a small sample of amniotic fluid is removed from the uterus and examined for chromosomal and genetic abnormalities. Typically, this surgery is carried out between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): A small sample of the placenta is removed via a process called chorionic villus sampling (CVS), and the results of the analysis are used to diagnose chromosomal and genetic problems. Typically, this surgery is carried out between 10 and 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Foetal echocardiography: The unborn heart and blood vessels can be seen in great detail thanks to a specialised form of ultrasound called foetal echocardiography. It can detect a wide range of foetal heart disorders, including congenital heart defects.
- Foetal MRI: The foetus is imaged in great detail using foetal MRI, a type of magnetic resonance imaging. It can be used to find a variety of foetal disorders, such as structural flaws and anomalies in the brain.
- Foetal blood sampling: During this procedure, a small sample of foetal blood is drawn and examined for chromosomal and genetic abnormalities. Typically, this surgery is carried out between weeks 18 and 22 of pregnancy.
- Doppler ultrasound: This specialist form of ultrasonography is used to assess the foetus’s blood flow. It can detect a wide range of foetal problems, including growth restriction and placental insufficiency.
- Foetal therapy: This is a specific form of care used to treat disorders in foetuses prior to birth. It might involve operations including foetal surgery, laser therapy, and balloon occlusion.
In order to offer comprehensive care for the mother and foetus, these procedures are used in conjunction with prenatal screening, genetic counselling, and routine obstetric follow-up. It’s crucial to remember that the field of foetal medicine is constantly changing, and new methods and treatments are being created all the time.

PROCEDURE
The following steps are commonly included in the foetal medicine process:
- Consultation: A foetal medicine specialist will evaluate your medical history and talk with you about any pregnancy-related worries you may have.
- Imaging: You may be subjected to a variety of imaging methods, including as ultrasound, foetal echocardiography, foetal MRI, or Doppler ultrasound, depending on your specific needs and the state of the foetus being assessed. These imaging procedures will create detailed images of the foetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid.
- Diagnostic procedures: A small sample of the amniotic fluid or placenta is taken for analysis during diagnostic procedures such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS), depending on the state of the foetus being assessed.
- Genetic counselling: If a genetic condition is detected, you might be referred to a genetic counsellor for additional assessment and counselling.
- Treatment: Depending on the state of the foetus, you can be given the choice of foetal surgery, laser therapy, or balloon occlusion.
- Follow-up: To keep an eye on the mother, the foetus, and the placenta during the pregnancy, routine follow-up sessions will be set up.
It’s vital to remember that the specific process will differ based on the circumstances of each instance and the state of the foetus being assessed.
BENEFITS
Some of the key advantages of foetal medicine include the following:
- Early diagnosis: Early diagnosis of foetal disorders is made possible by foetal medicine, which can significantly improve the result for both the mother and the unborn child. Early identification can improve treatment outcomes by lowering the risk of complications.
- Better patient care: During pregnancy, foetal medicine can be used to track the growth and development of the foetus, which can help to spot any possible issues early on. This can involve examining the placenta and amniotic fluid as well as keeping an eye out for any anomalies or indicators of growth restriction in the foetus.
- Reduced need for invasive procedures: The use of foetal medicine to non-invasively detect and diagnose a variety of foetal disorders can help to lessen the need for invasive procedures like chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis (CVS).
- Advanced imaging modalities: Doppler ultrasound, foetal MRI, foetal echocardiography, and ultrasound with Doppler can all be used in conjunction with foetal medicine to help diagnose and treat a wide range of diseases.
- Improved pregnancy outcomes: With the help of foetal medicine, early detection and treatment of foetal disorders can result in better pregnancy outcomes, such as a lower chance of preterm birth, a lower risk of stillbirth, and better neonatal outcomes.
- Individualized care: By taking into consideration the mother’s and her family’s particular requirements and preferences, foetal medicine enables a personalised approach to the diagnosis and therapy of foetal disorders.
- Remote access: By enabling the transmission of images for interpretation by experts in foetal medicine over great distances, foetal medicine technology has been used to raise the standard of care in remote and underdeveloped nations.