Overview
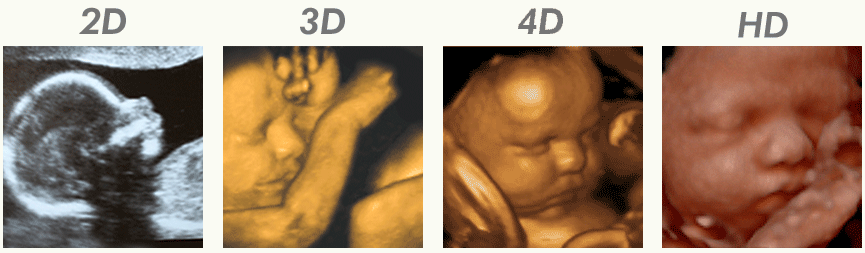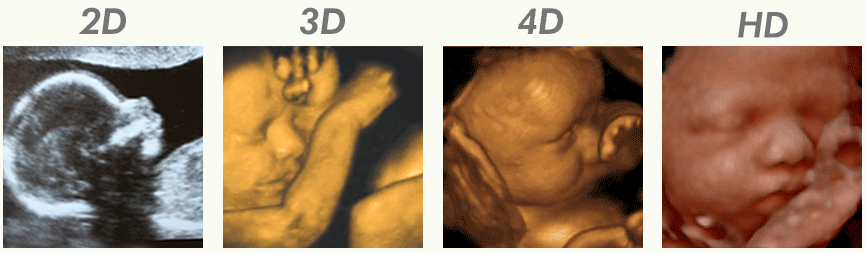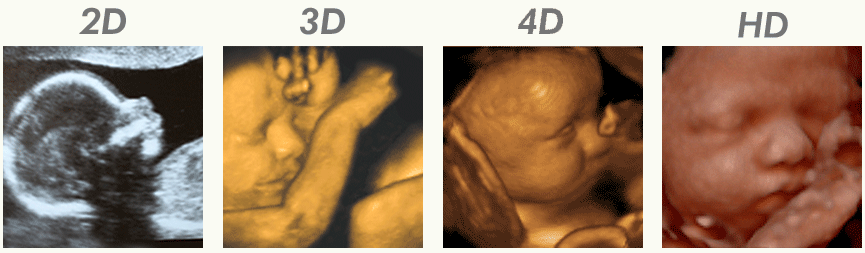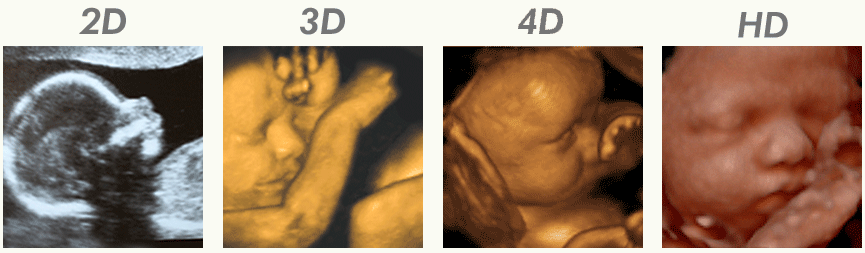
3D and 4D ultrasound are advanced forms of medical imaging that use sound waves to provide finely detailed images of the body’s internal organs and systems. 3D and 4D ultrasound give a more accurate, three-dimensional image of the area being looked at than 2D ultrasound, which only gives a flat, two-dimensional image.
3D ultrasound uses multiple sound waves to create a three-dimensional image of the inside of the body, which enables medical professionals to more clearly observe the shape and structure of organs and other internal structures. This technique is very helpful for locating and detecting anomalies, such as tumours or cysts, as well as for keeping track of a fetus’s growth during pregnancy.
4D ultrasound, also referred to as “dynamic 3D ultrasound,” expands on the idea of 3D imaging by including the dimension of time. This enables medical professionals to observe the motion and operation of internal organs, such as the heartbeat of a foetus or the flow of blood through its blood vessels. During pregnancy, 4D ultrasound can also be used to look for issues with the placenta, umbilical cord, or amniotic fluid.
CONDITIONS DIAGNOSED VIA 3D AND 4D ULTRASOUND
- Prenatal foetal development: 3D and 4D ultrasounds can provide medical professionals with detailed views of the foetus, allowing them to track its growth and development and look for any potential anomalies.
- Internal organ problems: 3D and 4D ultrasound can be used to analyse the structure and function of organs such as the liver, kidney, and pancreas, as well as to help find and diagnose internal organ abnormalities like tumours or cysts.
- Placental and umbilical cord problems: Problems with the placenta and umbilical cord can be found using a 4D ultrasound, such as placental insufficiency, which can cause poor foetal growth or preterm delivery.
- Amniotic fluid problems: Problems with the amniotic fluid, such as polyhydramnios, which is an overabundance of amniotic fluid, or oligohydramnios, which is an underabundance of amniotic fluid, can also be found with 4D ultrasound.
- Cardiac conditions: 4D ultrasound can be used to evaluate the shape and performance of the heart, as well as to detect any foetal congenital heart problems.
- Gynaecological conditions: 3D and 4D ultrasound can be used to assess the composition and efficiency of the female reproductive system, as well as to identify diseases such as polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis.
- Musculoskeletal disorders: 3D and 4D ultrasound can be used to assess the composition and functionality of muscles, tendons, and ligaments, as well as to identify diseases such as tendinitis or muscle tears.
PROCEDURE
- Preparation: You will be required to fill out a medical history form prior to the operation, and you might be requested to drink water to fill your bladder as this can aid in providing sharper images of the uterus and ovaries.
- Positioning: To help the sound waves pass through your skin and into the room, you will be asked to lie down on an examination table. The images will be produced when the ultrasound transducer has been placed on your skin and moved around.
- Imaging: The ultrasound machine will transmit sound waves into the body during the operation; when the waves are reflected back to the machine, images of the interior organs and structures are produced. The photos can be saved so that they can be studied later and will be shown on a screen.
- Duration: Depending on the area being checked and the complexity of the case, the process normally lasts between 30 minutes and an hour.
- Safety: Ultrasound in 3D and 4D is a safe alternative to other imaging methods because it is fully non-invasive and does not subject the patient to ionising radiation.
- Results: After reviewing the photos, your doctor or radiologist will go over the findings with you. Additionally, they will give you copies of the pictures for your records.
- Follow-up: Your doctor could suggest more tests or therapy based on the findings. It’s crucial to adhere to your doctor’s recommendations and make any suggested follow-up appointments.

ADVANTAGES
- Better visualisation: 3D and 4D ultrasound produce intricate, three-dimensional images of interior organs and body systems, which can give the area being examined a more realistic appearance. This can make it easier for medical professionals to recognise and diagnose a variety of diseases, including foetal abnormalities and pregnancy difficulties.
- Real-time imaging: 3D and 4D ultrasound technology can be used to show doctors how inside organs move and operate, such as a foetus’s beating heart or blood flowing via blood veins.
- Non-invasive: Compared to other imaging methods, 3D and 4D ultrasound are fully non-invasive and do not subject the patient to ionising radiation.
- Better bonding: 4D ultrasound, in particular, allows parents to see their unborn child’s face characteristics and movements, which can aid in the development of a stronger kinship between them and their child as well as a deeper sense of connection to the pregnancy.
- Cost-effective: Ultrasound in 3D and 4D is comparatively inexpensive and widely accessible.
- Early detection: 3D and 4D ultrasound can find problems and abnormalities early on, which makes it more likely that the patient will respond well to treatment and get better.
- Reduce the need for extra tests: 3D and 4D ultrasounds can give a lot of information about many different diseases, and in some cases, they can reduce the need for invasive procedures or other tests.